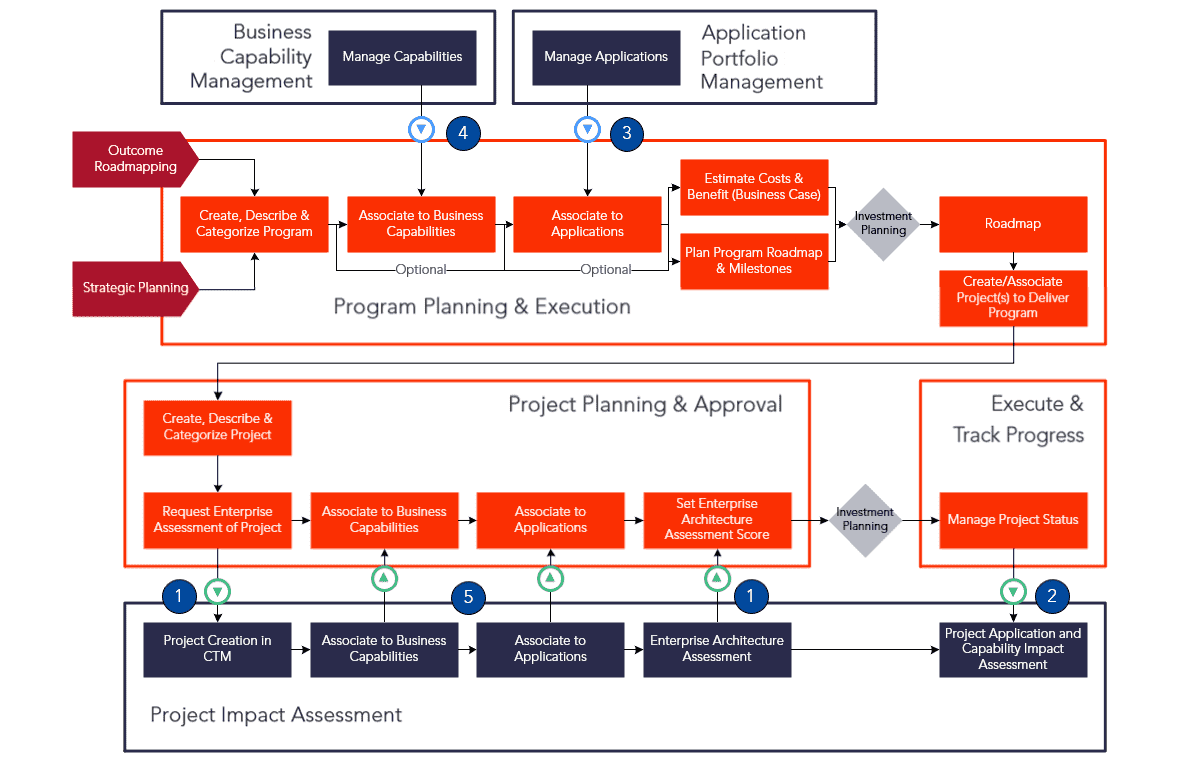
Enterprise Architecture process flows
Overview
This guide provides a comprehensive look at how organizations can use Planview’s enterprise architecture (EA) capability to align technology with strategy and drive business transformation. Learn how to assess architecture, manage application and capability portfolios, and support strategic planning through integrated workflows and cross-functional collaboration. From evaluating new demands to modeling trade-offs, you’ll discover best practices and key processes for roadmapping, rationalization, and capacity planning. Whether you're tracking application impact, aligning capabilities with strategy, or informing investment decisions, this guide will help enterprise architects and portfolio leaders collaborate more effectively and deliver measurable outcomes.
Connection points
|
1. Enterprise Architecture Assessment
2. Execution Alignment
3. Application Inventory
|
4. Capability Alignment
5. Project Associations
|
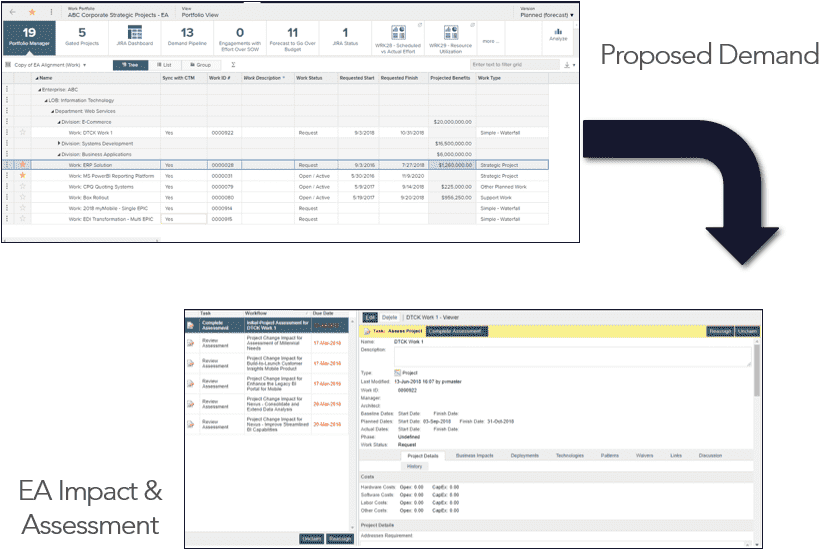
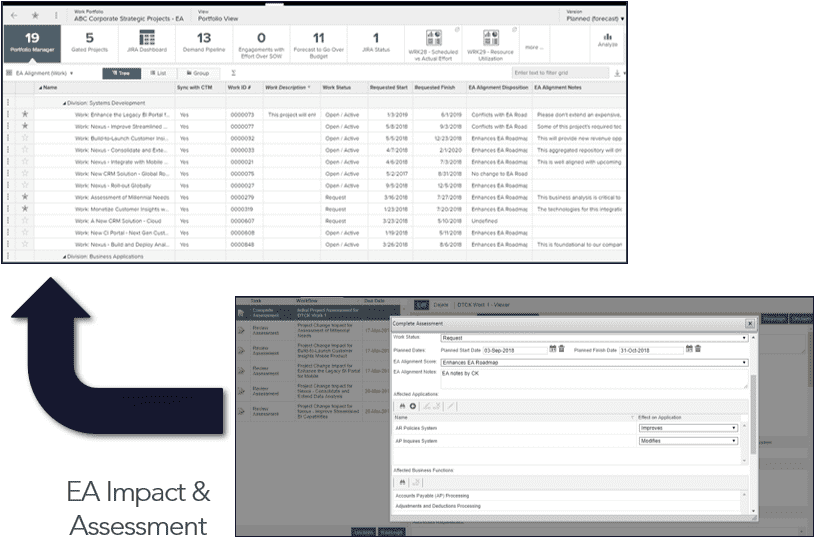
Demand management
Challenges
- EAs do not have enough visibility into the demand pipeline
- Results in realizing critical dependencies and gaps AFTER project approval process
- EAs need to be able to see demands as they are coming in so that they can:
- Map those demands to existing business capabilities
- Identify gaps in the current capability portfolio to create new capabilities
The solution
- EAs can provide an enterprise-wide view of planned investments through the use of EA demand assessments
- Limits the potential problems that will arise from misaligned programs by ensuring investment alignment to business and tech architecture at the front end of the planning process
- Helps to drive strategic alignment of investments
- Results in overall project delivery improvement through reduction of project risk
- Promotes architectural standards throughout the organization
| Initiate Demand | EA Assessment | Assessment Results |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
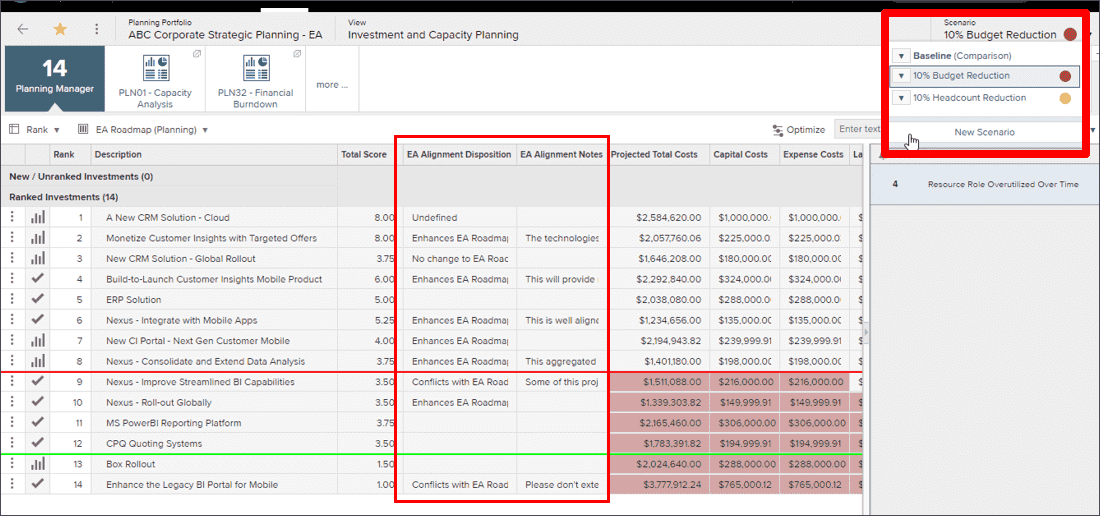
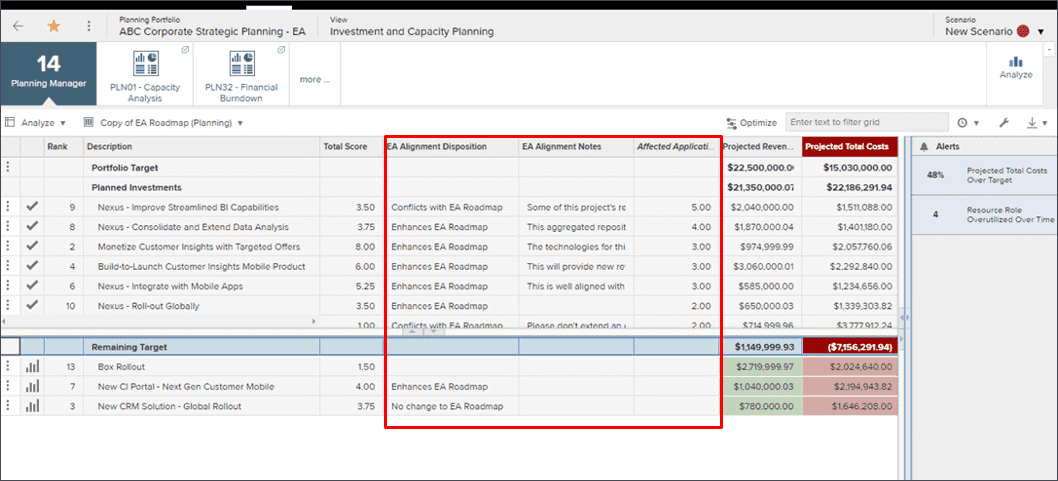
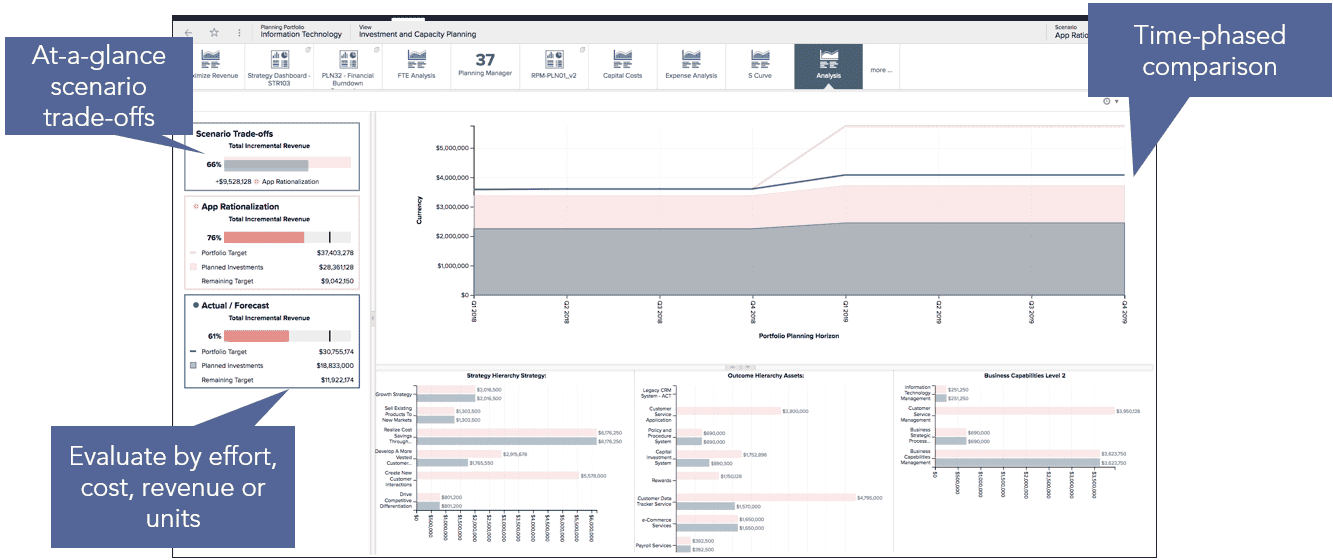
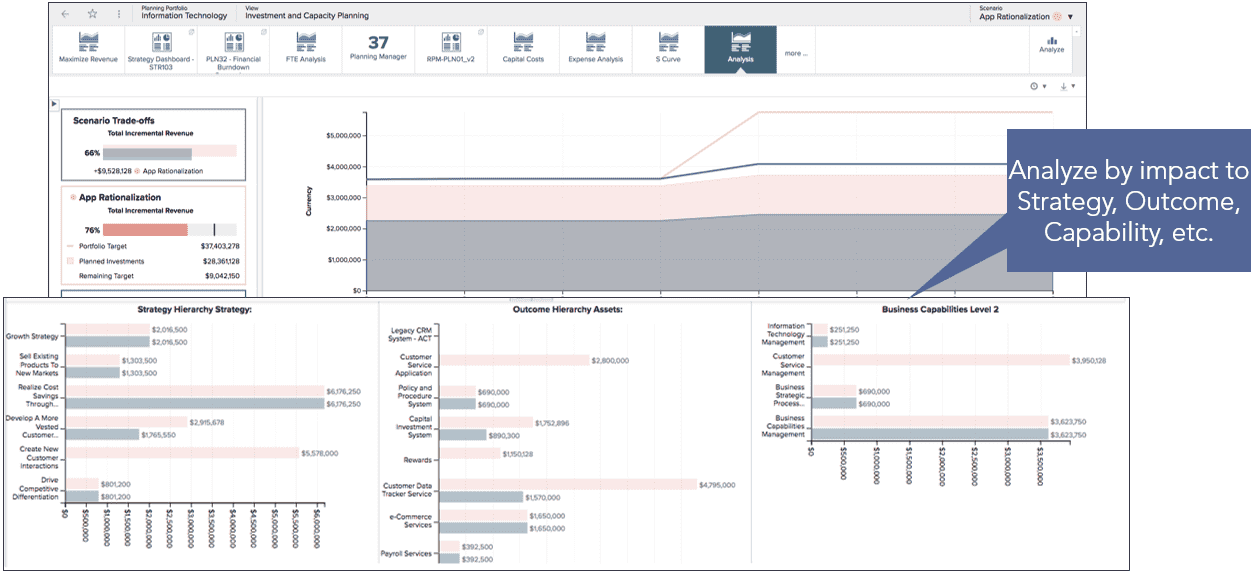
Capacity planning
Challenges
- Limited capacity requires trade-offs to be made but its not always easy to fully understand the impacts of those decisions
- PMOs and EAs need an easy way to understand the portfolio:
- from different perspectives
- and impacts on other portfolios
The solution
- Create investment scenarios to evaluate alternative approaches to determine the optimal investment plan
- Understand which scenario accomplishes driving revenue, controlling spend, managing capacity, or all of the above
- Provide summary level information to leadership at appropriate level
- Model investment impacts across strategies, capabilities and technology
- Understand the impacts of trade-offs about what you are or are not delivering
- Communicate how trade-offs affect achieving strategies and maturing business capabilities
| Create Scenarios | Investment and Capacity Planning |
|
|
|
| Model Trade-Off Decisions | |
|
|
|
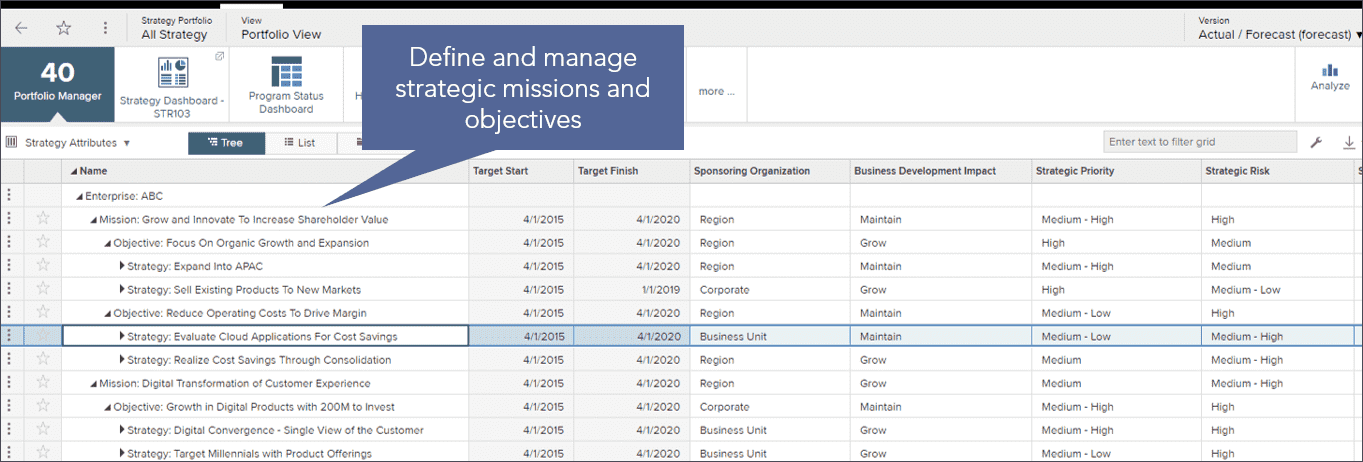
Roadmapping
Challenges
- Strategy disconnected from delivery
- Not delivering intended outcomes
- Disjoint between IT and business Initiatives leading to misalignments in the portfolio
- Missed deadlines
- Unintended consequences
The solution
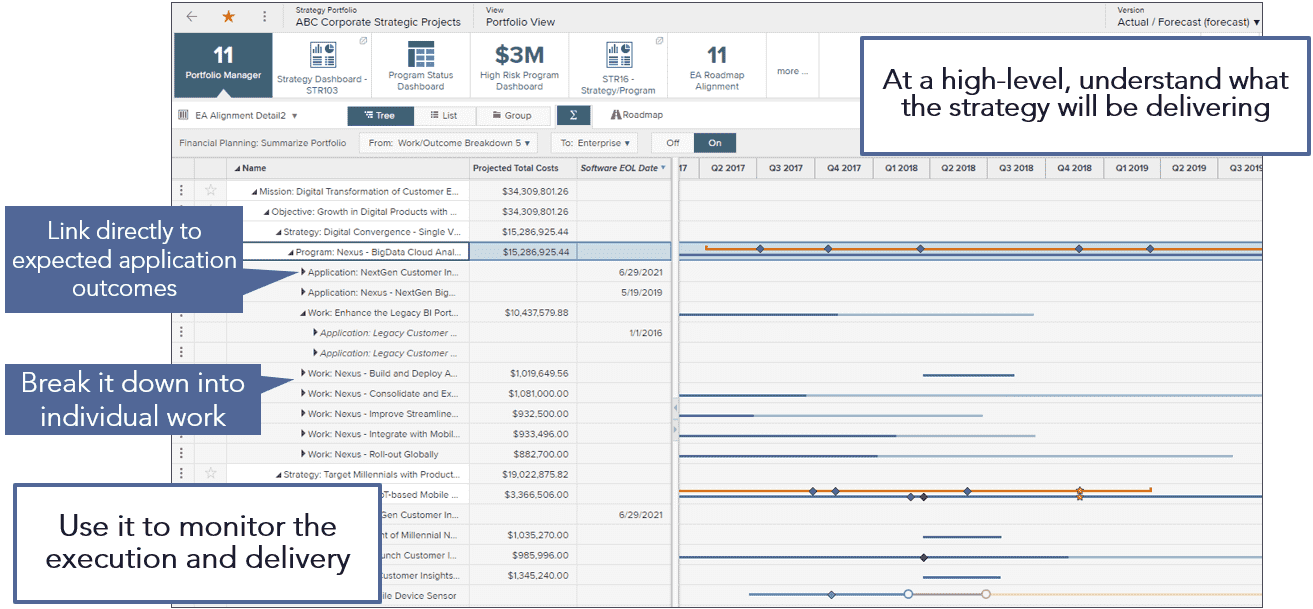
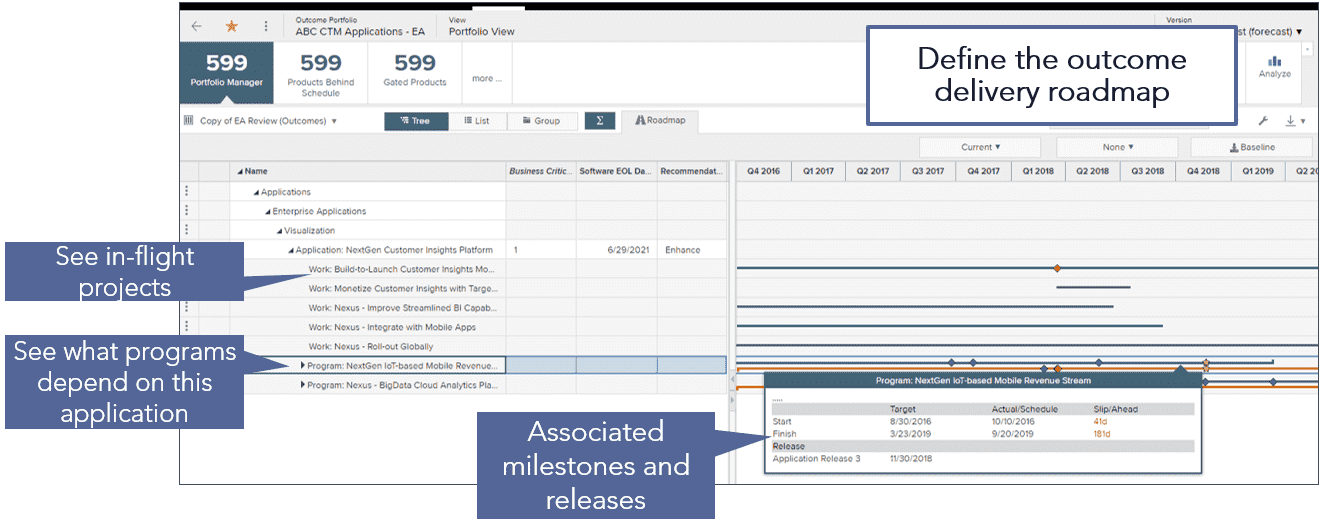
- Realize strategy through integrated roadmaps that describes how the programs, projects, applications, and products will deliver on strategic and organizational goals.
- Monitor the progress of execution against strategic plans
- Define roadmaps that provide an integrated view of proposed investments with strategies and project’s impact to capabilities and applications.
- Results in better project decisions and use of technology
| Define Strategies | Create the Strategic Roadmap | Create the Outcome Roadmap |
|
|
|
|
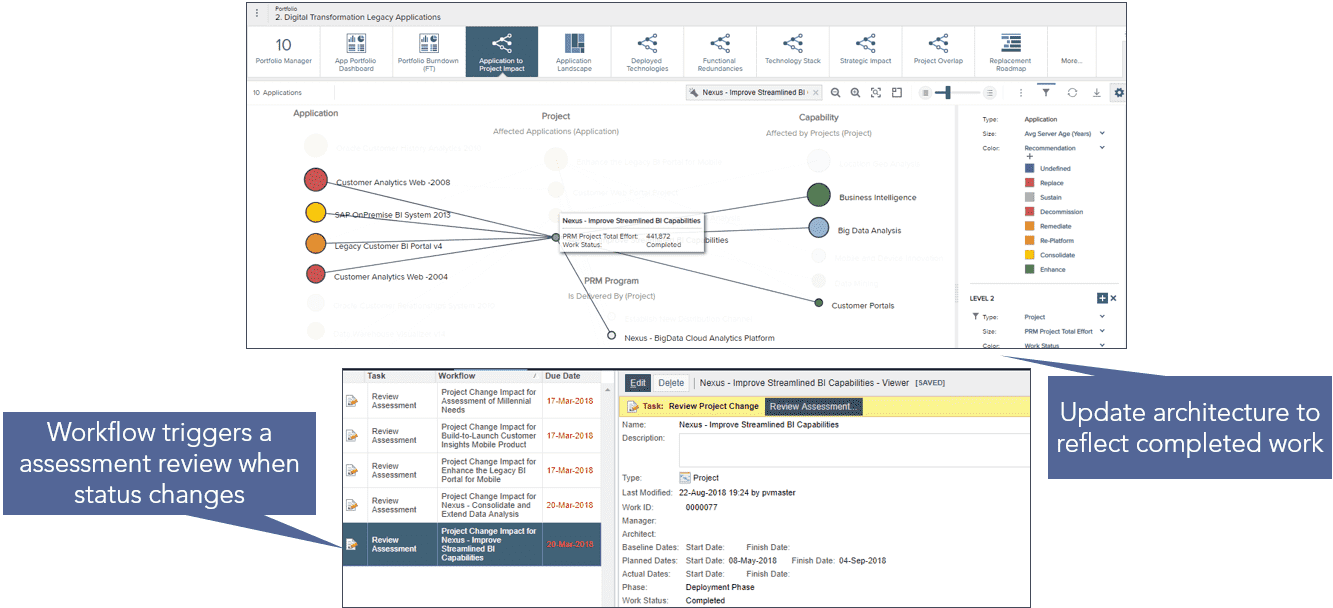
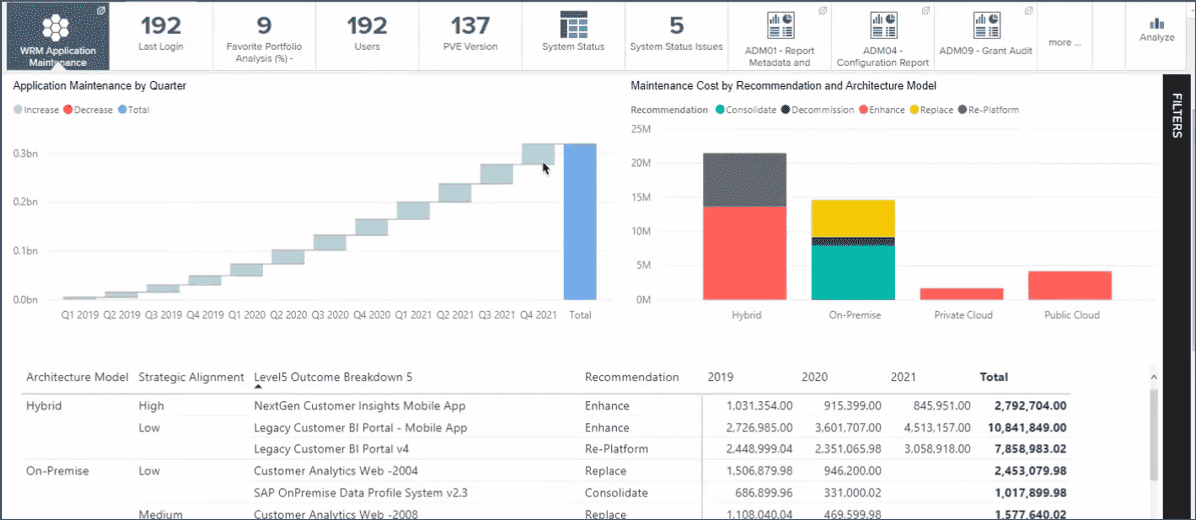
Work and application rationalization
Challenges
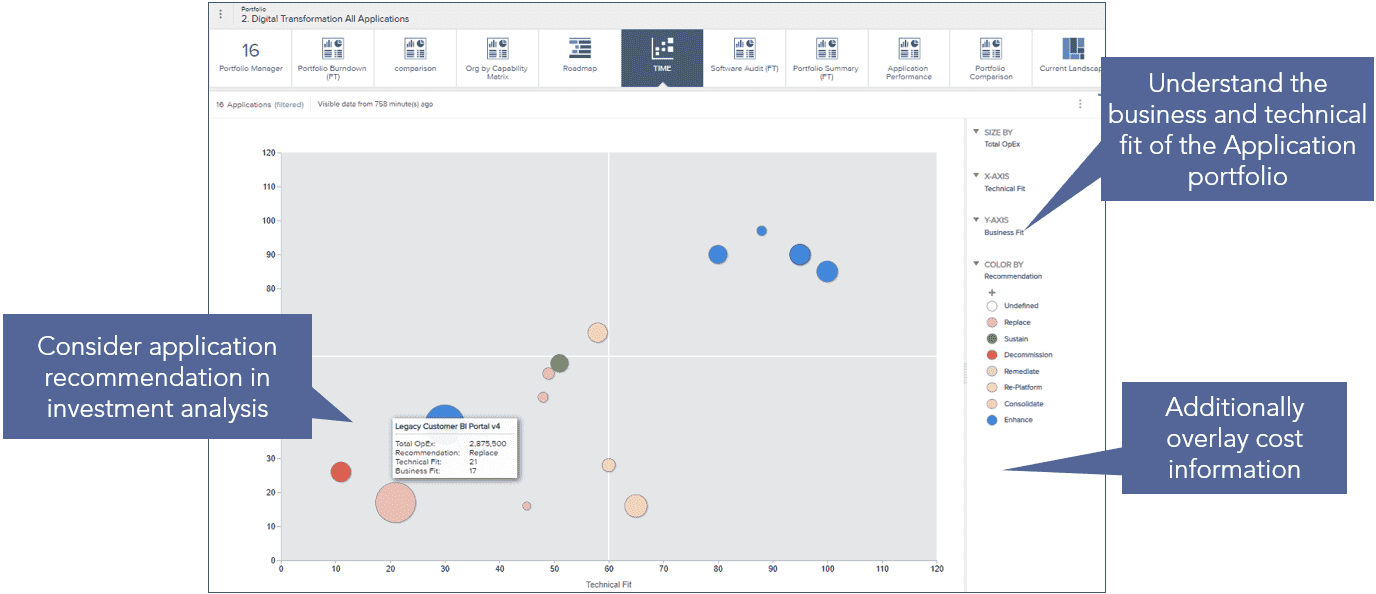
- No visibility into the application portfolio leads to application complexity and sprawl
- Difficult to determine the right technology, for the right purpose, at the right time
- Technology utilization is not maximized
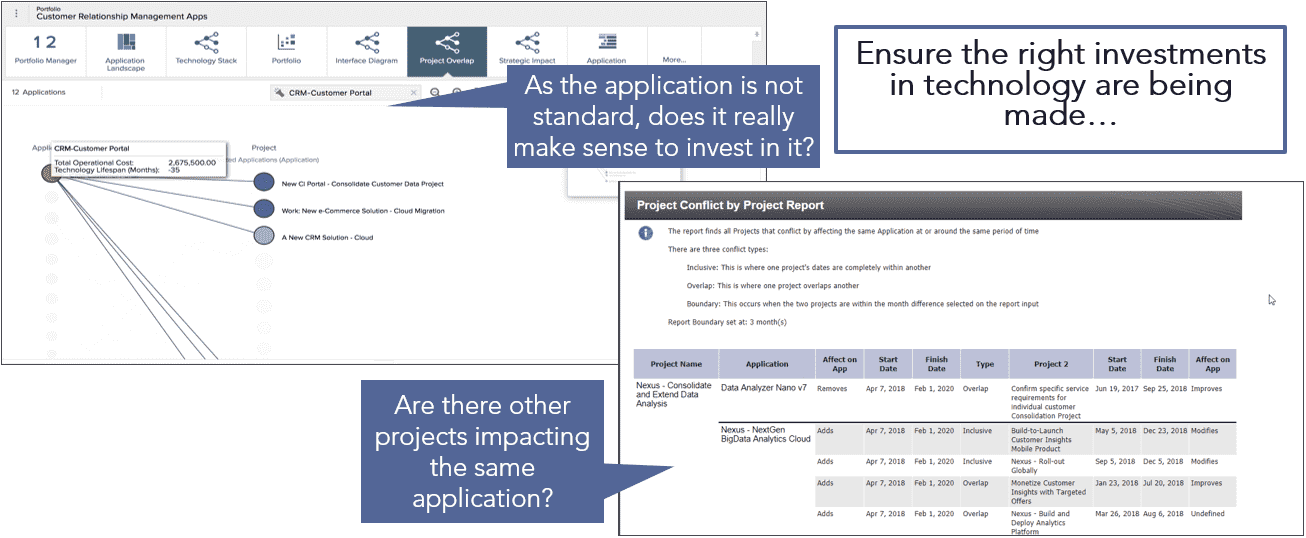
- Too many similar initiatives; portfolio interdependencies not understood
- Need to identify project overlaps, impacts, and dependencies to avoid unexpected down-stream impacts
The solution
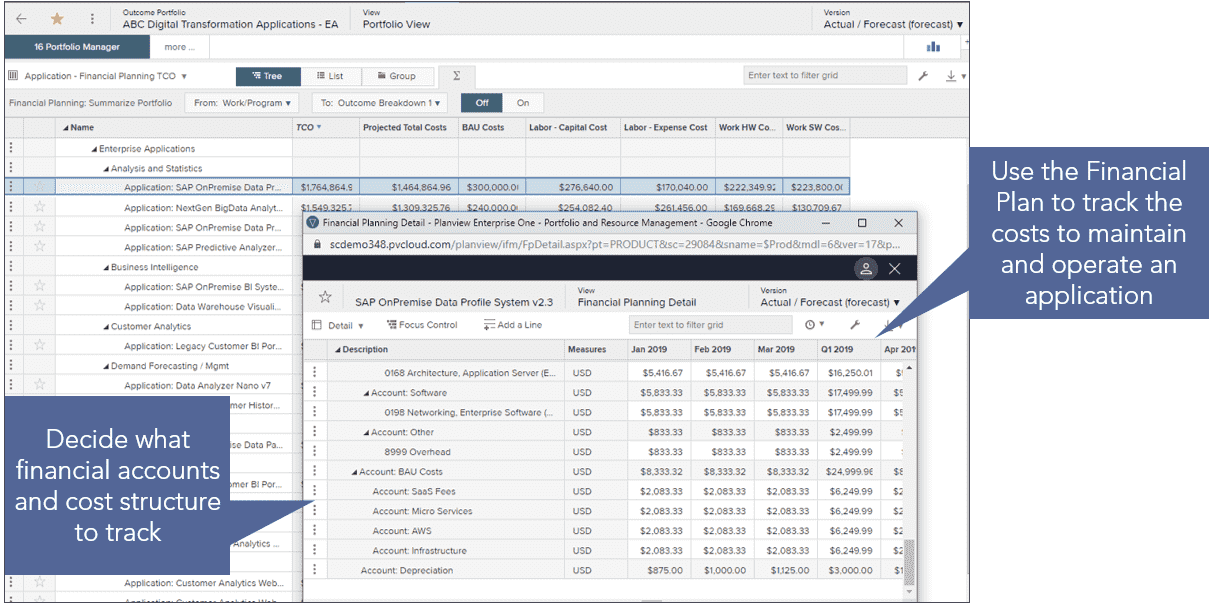
- Drive cost out of IT portfolios
- Leverage existing technologies and applications to meet the organizational demand (stop buying new stuff), achieving more rapid fulfillment of business need
- Identify projects that can be merged or no longer needed
- Identify reuse opportunities for applications and technology
- Track progress against application and technology lifecycles by integrating project execution with technology planning
- Drives more timely achievement of the to-be state
| Track Application Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) | Analyze investments in context of the Application Landscape | Assess investment impact against technology portfolio |
|
|
|
|
| Keep up to date with project status | Measure Application Costs Over Time |
|
|
|
Best practices
Involve the right people
Build relationships with your colleagues and multidisciplinary teams who make decisions about business model and operating model changes, develop strategies for internal and customer-facing products and services, and execute process reengineering and capability enabling technologies—these are your primary internal customers. Understanding capability gaps and requirements and delivering the right outcomes and results can only be achieved by collaborating with different roles across an organization and with customers.
Create a strategic business outcome roadmap
Prepare a roadmap that outlines how the organization’s business and operational model can be modified to fulfill its strategic objectives. Share the change roadmap and the affected value streams, business capabilities, applications, and technologies required to achieve business outcomes with your PMO colleagues and develop a communication plan that addresses the needs of all stakeholders.
Focus on business architecture
Focus on aligning customer’s need in products and services with the supporting technologies, services, locations, applications, and other assets to achieve business outcomes, rather than on IT-driven architecture. As enterprise architects dedicate more time to customer journeys and the business architecture and business-related portfolios, they can support the corporate strategy, deliver better outcomes, and create a portfolio of transformation programs that is more architecturally sound.
Create and document a target output list
Create and document a target output list and provide your stakeholders with visual representations of the architecture using enterprise architecture management software.
Limit data collection
Extract the maximum amount of value from the least amount of data. Ensure that your data collection focuses on what is necessary to produce valuable stakeholder outputs based on your target outputs list.
Determine data ownership
Identify data owners who will oversee a subset of the target data items. Ensure that the data collected is complete, accurate, and consistent.
Deliver incrementally
Successful enterprise architecture management programs deliver small successes in regular intervals. Identify the kinds of questions and outputs that were answered and announce each success separately.