How does Hub change detection work?
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
Last Updated: | Applicable Hub Versions: All
Answer
Introduction
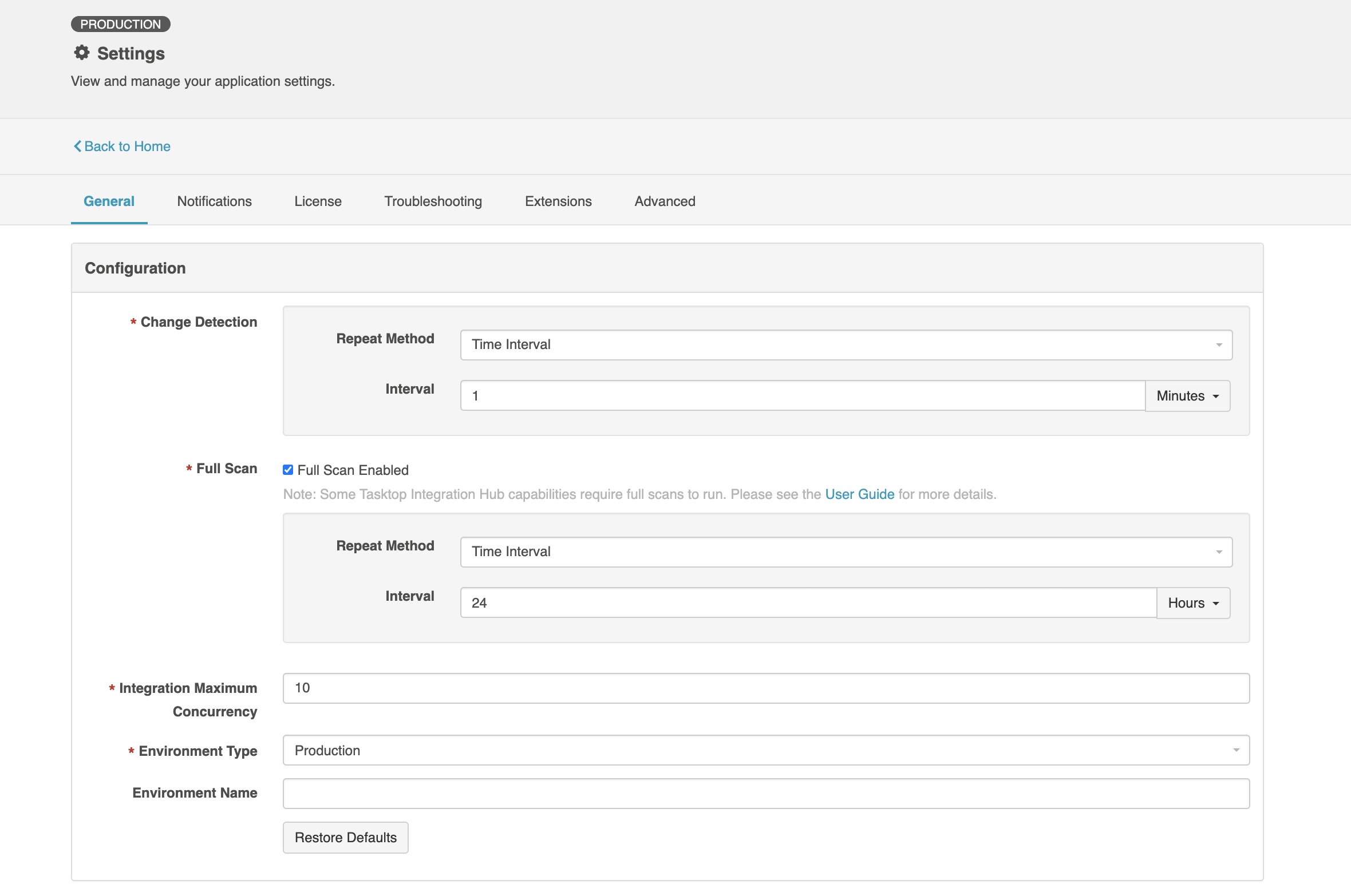
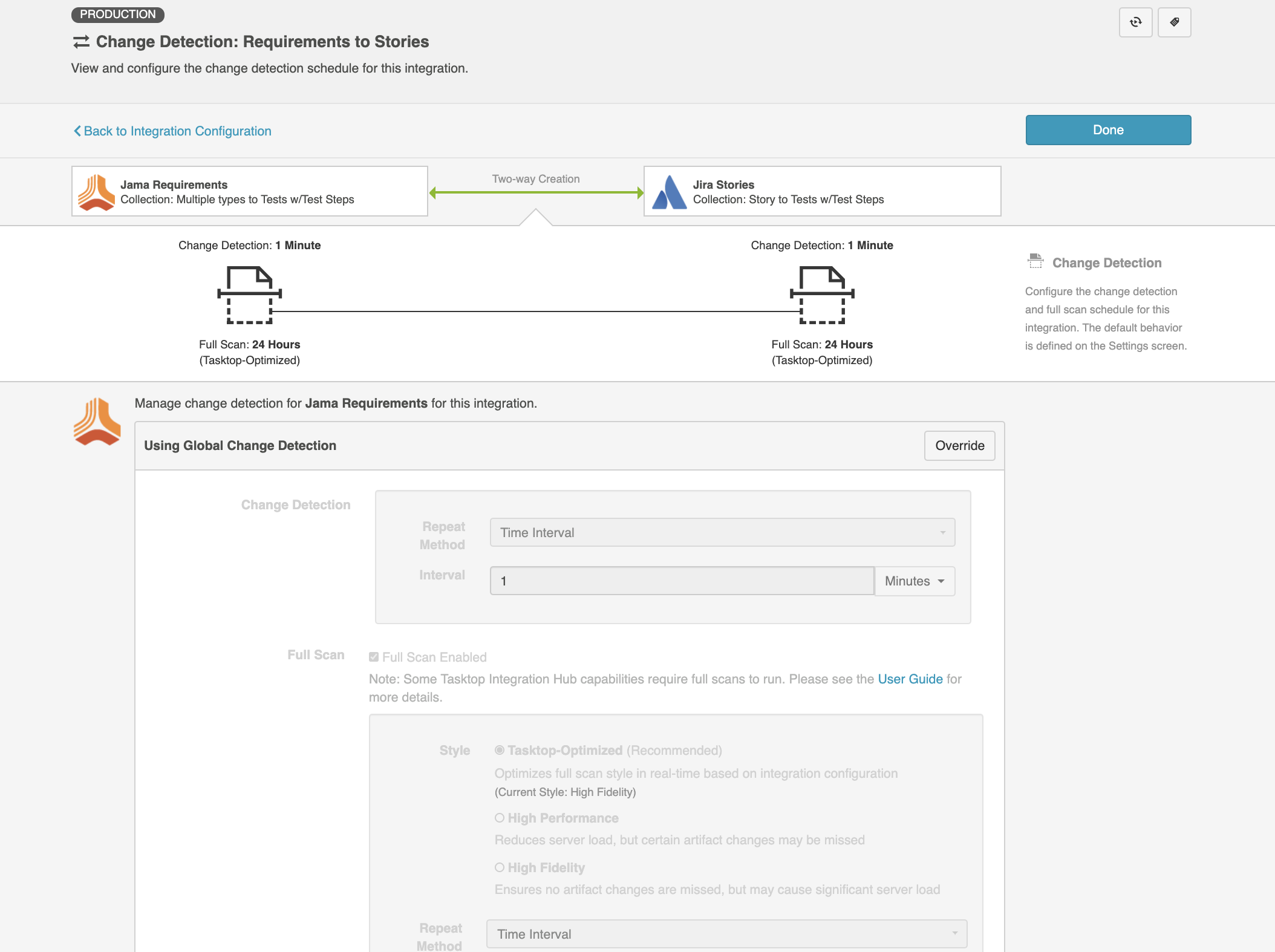
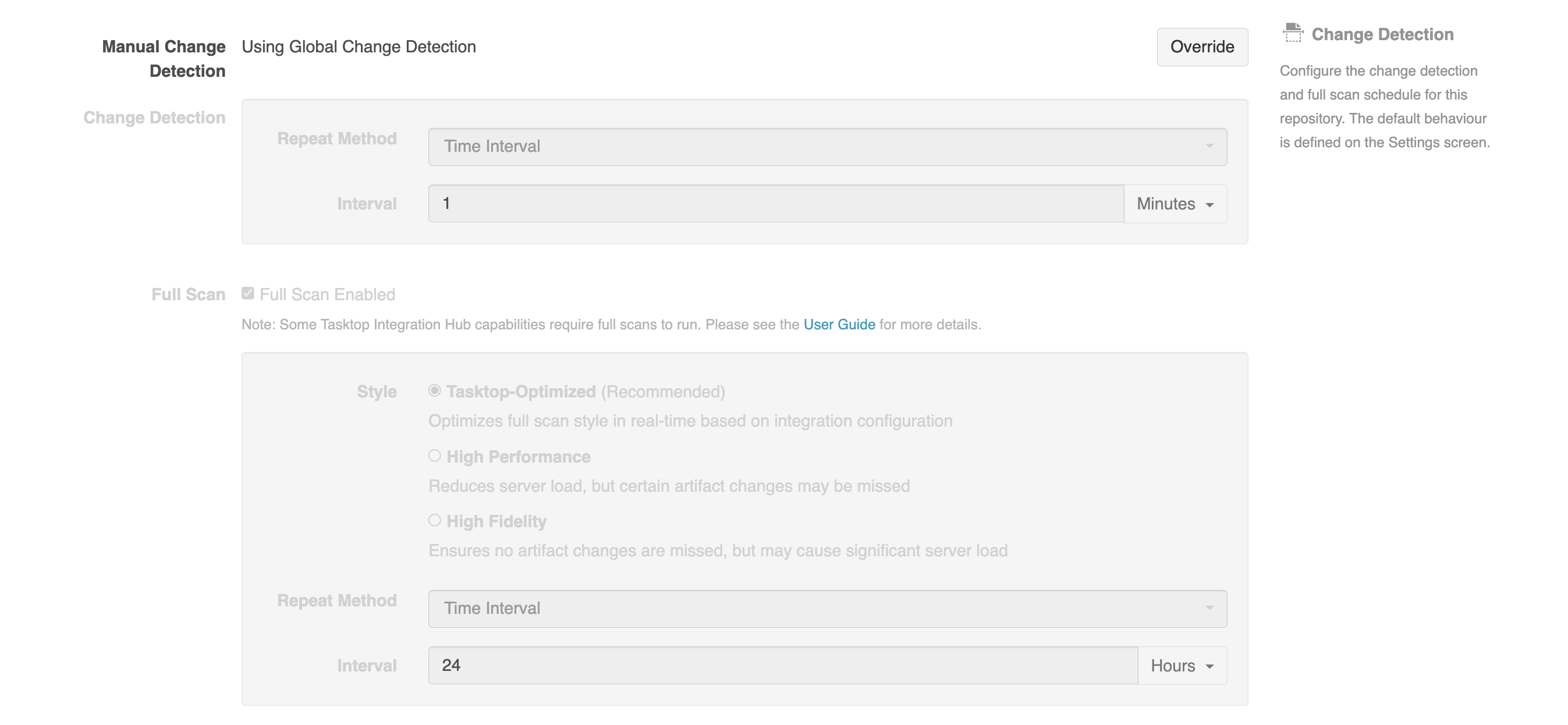
Hub can poll for data in each external repository using three different methods: change detection, high performance full scan, and high fidelity full scan. Within Hub, you can set global change detection and full scan intervals on the Settings screen. The full scan style (either high fidelity or high performance) is chosen by Hub on an integration-by-integration basis (you will see this referred to as "Tasktop-Optimized" in the UI), but can also be manually configured for each integration. You can also set integration-specific change detection and full scan intervals and repository-specific change detection and full scan intervals that will override the global settings.
Note: When configuring change detection settings, integration-level change detection has the highest precedence, followed by repository-level change detection, and then global change detection. This means that if integration-level change detection is configured, the integration-level setting will always be used (even if repository-level or global settings are configured). If no overrides are set, change detection will default to the global settings.
Here’s a metaphor to help understand the differences between the change detection, high performance full scan, and high fidelity full scan:
- Change Detection is the daily maintenance you do on your home: putting clothes away, wiping down the counter, taking the trash out. It picks up the vast majority of artifact changes without putting high server load on your external repositories, but it can miss some updates due to third party limitations.
- High Performance Full Scan is your monthly deep cleaning: mopping the floors, wiping down windows, really trying to clean out some of the dirt you don’t always get. It has only a slightly higher performance impact than normal change detection and is able to pick up some changes which may have been missed as well as trigger certain Hub features like the Twinless Artifact Update.
- High Fidelity Full Scan is your monthly deep cleaning on steroids — really dusting those cobwebs off of those hard-to-reach spots. This style should pick up all artifact changes, but the trade off is that it has a high performance impact due to the amount of work Hub must do to query for all artifact changes.
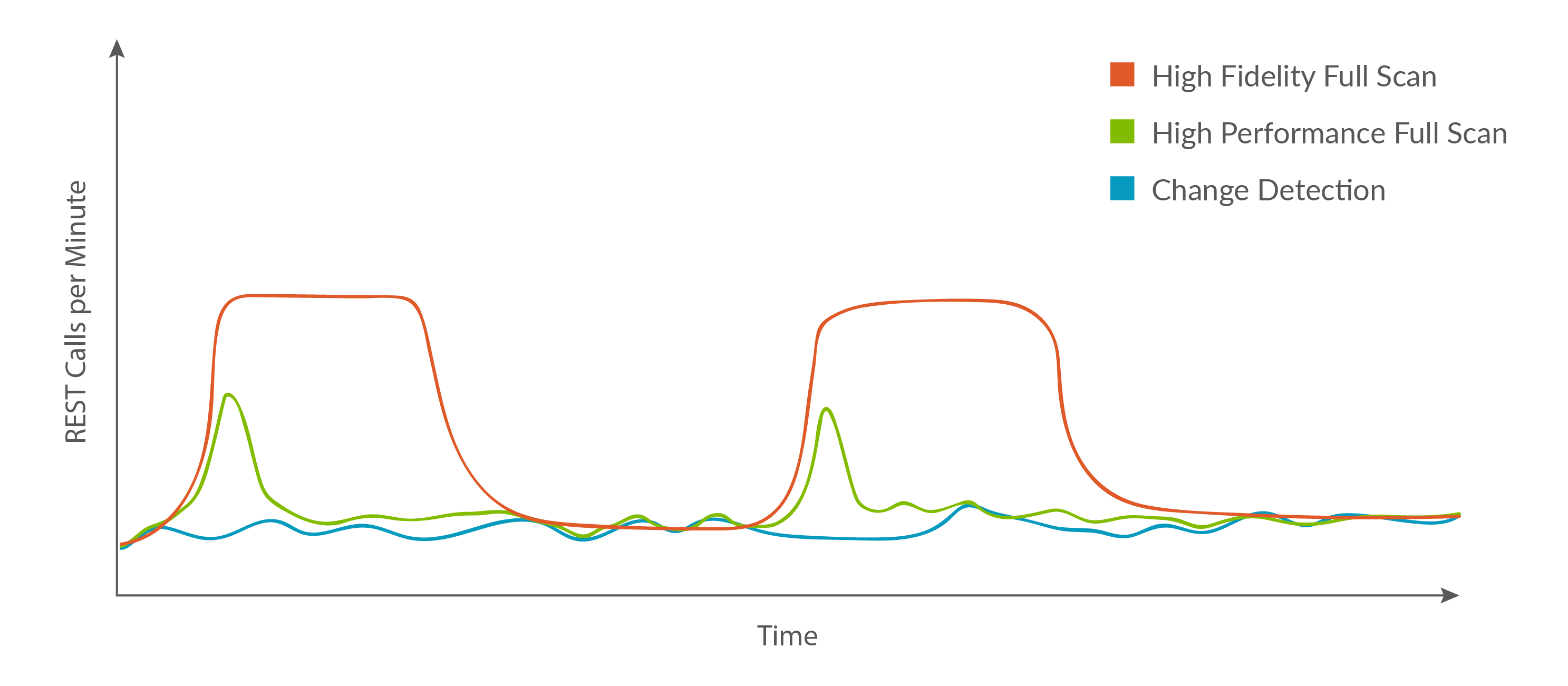
Below is a graph showing the relative performance impacts of each process. Note that Change Detection and High Performance Full Scan have relatively similar, low performance impacts, while High Fidelity Full Scan has a higher and more sustained performance impact. You can read below to learn more about how each process works.
Also note that when an integration is first started, you may see a high performance impact, especially if the scope is very large (e.g., ITSM tools or a system like Jira which may have many users).
Change Detection
Change Detection is necessary for all customers in all integration scenarios. It is the default means by which Hub recognizes updates to artifacts in external repositories and is able to propagate those changes. The change detection interval should be frequent, for example running once every 1-5 minutes.
How does Change Detection work?
-
Hub retrieves a short list of artifacts with essential information, like ID and Last Modified. The list is ordered by Last Modified date, with most recently updated artifacts at the top. The length of the list depends on the repository, but there are typically about 50 artifacts per list.
-
Hub compares the Last Modified field for each artifact on the list with the one stored in Planview Hub.
-
If there is a difference, Hub will add the artifact to the synchronization queue to be fully retrieved and processed.
-
Hub repeats the steps above for the next artifact on the list.
-
Though change detection typically only requires that Hub review one list of artifacts, if there still appear to be artifacts with changes once the first list is reviewed, Hub will retrieve another list and start again from step 1.
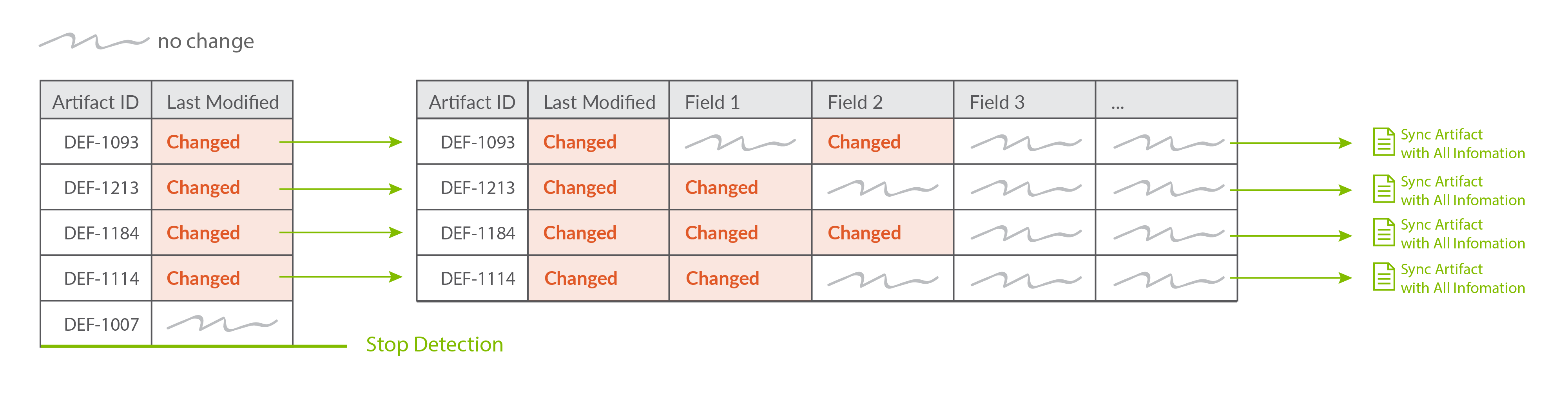
High Level Summary
-
 Short time interval (1-5 min)
Short time interval (1-5 min) -
 Light Performance impact
Light Performance impact -
 Some changes may be missed*
Some changes may be missed* -
 Some twinless artifact updates could be missed*
Some twinless artifact updates could be missed*
*for certain connectors/configurations, due to third party limitations.
High Performance Full Scan
There may be times when a more robust means of determining artifact changes is necessary — either to pick up rare missed artifact changes or to take advantage of a Hub features such as Twinless Artifact Update.
The High Performance Full Scan is sufficient for most customer use cases and has only a slightly larger impact on repository server load than a normal Change Detection query.
Instead of retrieving a short list of artifacts that Hub believes may have changed, the High Performance Full scan retrieves a list containing essential information (ID and Last Modified field) for all the artifacts that have synchronized in the integration, but only fully retrieves and synchronizes those artifacts that have been marked as updated.
A typical high performance full scan is configured to run once every 1-24 hours.
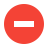
How does High Performance Full Scan work?
-
Hub retrieves a list of all artifacts that have synchronized in the integration with essential information like ID and Last Modified. The list is ordered by Last Modified date, with most recently updated artifacts at the top.
-
Hub compares the Last Modified of every retrieved artifact with every one stored in the Planview Hub
-
If there is a difference, Hub will add the artifact to the synchronization queue to be fully retrieved and processed.
-
Hub repeats the steps above for each artifact in the list.
-
Based on this process, Hub will identify any artifacts that have been removed from the integration. These are then processed as ‘remove’ events for Enterprise Data Stream integrations, or can trigger Twinless Artifact Update, if that feature has been configured.
High Level Summary
-
 Longer time interval (1-24 hr)
Longer time interval (1-24 hr) -
 Slightly larger performance impact than Change Detection
Slightly larger performance impact than Change Detection -
 Triggers Twinless Artifact Update
Triggers Twinless Artifact Update -
 Triggers ‘Remove’ events for Enterprise Data Stream integrations
Triggers ‘Remove’ events for Enterprise Data Stream integrations -
 Newly eligible artifacts from updated artifact filtering or routing will not be picked up*
Newly eligible artifacts from updated artifact filtering or routing will not be picked up* -
 Rare changes may be missed**
Rare changes may be missed**
*because Full Scan only pulls in artifacts that have already synchronized, artifacts that are newly eligible for integration based on updated artifact filtering or routing will not be picked up. These artifacts will only be processed by clicking the 'process all artifacts' button, or when a new integration-eligible change is made to them.
**for certain connectors/configurations, due to third party limitations.
High Fidelity Full Scan
The High Fidelity Full Scan is only needed if you are flowing certain fields in certain repositories whose changes cannot be detected via the other two methods due to third party limitations.
This scan retrieves every artifact that has synchronized in the integration and then inspects each artifact to determine if a change needs to be propagated.
Retrieving every artifact (rather than a simple list of 'ID' and 'Last Modified' for each artifact) generates a sizable repository load.
A typical high fidelity full scan is once every 24 hours or more.
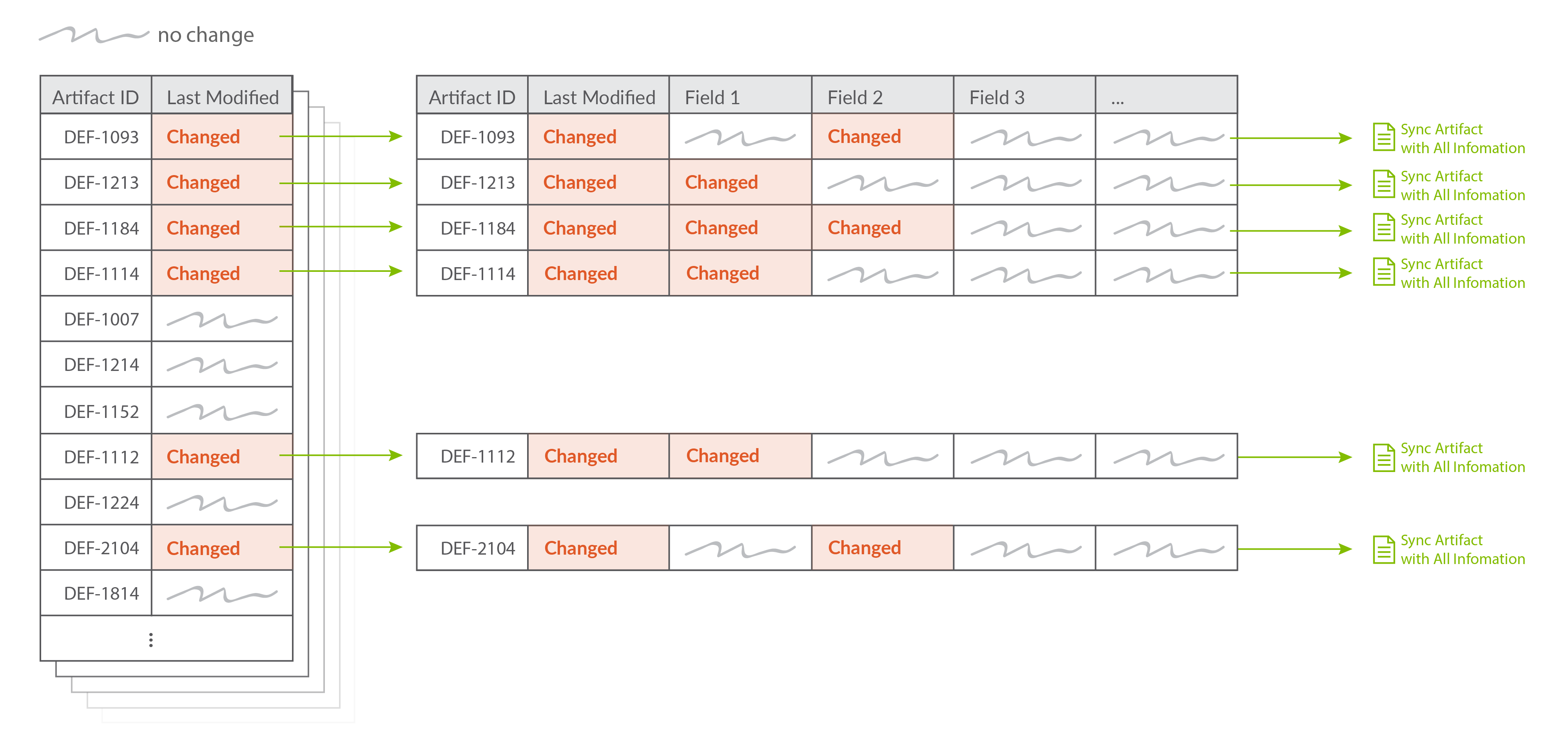
How does High Fidelity Full Scan work?
-
Hub retrieves a list of all artifacts that have synchronized with essential information like ID and Last Modified.
-
Hub retrieves the first artifact in the list with complete data.
-
Hub compares the complete data of the retrieved artifact with the complete data of the same artifact stored in Hub.
-
If Hub detects that the artifact has been changed, the artifact is added to the synchronization queue to be synchronized per the integration configuration.
-
Hub repeats steps 2-4 until all artifacts that have previously synchronized are retrieved.
High Level Summary
-
 Long time interval (24 hr+)
Long time interval (24 hr+) -
 High Performance impact
High Performance impact -
 Triggers Twinless Artifact Update
Triggers Twinless Artifact Update -
 Triggers Remove events for Enterprise Data Stream integrations
Triggers Remove events for Enterprise Data Stream integrations -
 Will catch any missed artifact changes on artifacts that have previously synchronized
Will catch any missed artifact changes on artifacts that have previously synchronized -
 Newly eligible artifacts from updated artifact filtering or routing will not be picked up*
Newly eligible artifacts from updated artifact filtering or routing will not be picked up*
*because Full Scan only pulls in artifacts that have already synchronized, artifacts that are newly eligible for integration based on updated artifact filtering or routing will not be picked up. These artifacts will only be processed by clicking the 'process all artifacts' button, or when a new integration-eligible change is made to them.
How does the “Process All Artifacts” Button fit into all this?
On the Field Flow screen of each integration, you will see a ‘Process All Artifacts’ button. This button allows you to force through updates from one collection in your integration. This can be useful if you add a new field mapping to your configuration or if you change your artifact routing or artifact filtering criteria to add new artifacts to your integration.
When Process All Artifacts is clicked, Hub forces a special High Fidelity Full Scan to run at the next change detection interval. Unlike a typical High Fidelity Full Scan, this will scan ALL artifacts within the collection (regardless of whether they have synchronized or not). This means that it will pick up artifacts that are newly eligible for the integration based on updated routing or filtering. As such, users should expect that this feature can lead to high server load on the external repositories.

