Deprecation of NTLM FAQ
Last Updated: September 27, | Applicable Hub Versions: All
Deprecation of NTLM
Due to security concerns (see below for details), Planview has decided to deprecate all uses of NTLM within the Flow Fabric connectors on October 1, 2023.
Specifically, this affects the following connectors, and only connections to on-premise instances:
- Digital.ai Agility
- Microsoft Azure DevOps
- Microsoft SharePoint
- Microsoft Project Server
All connectors do support alternative authentication methods.
Do I need to take any action?
In most cases, the deprecation will be completely transparent. In rare cases, repositories may be configured to only support NTLM based authentication. You are able to verify this using a new option introduced in the connections screens of the affected connectors as follows:
- Open the connection setting of the connector in question.
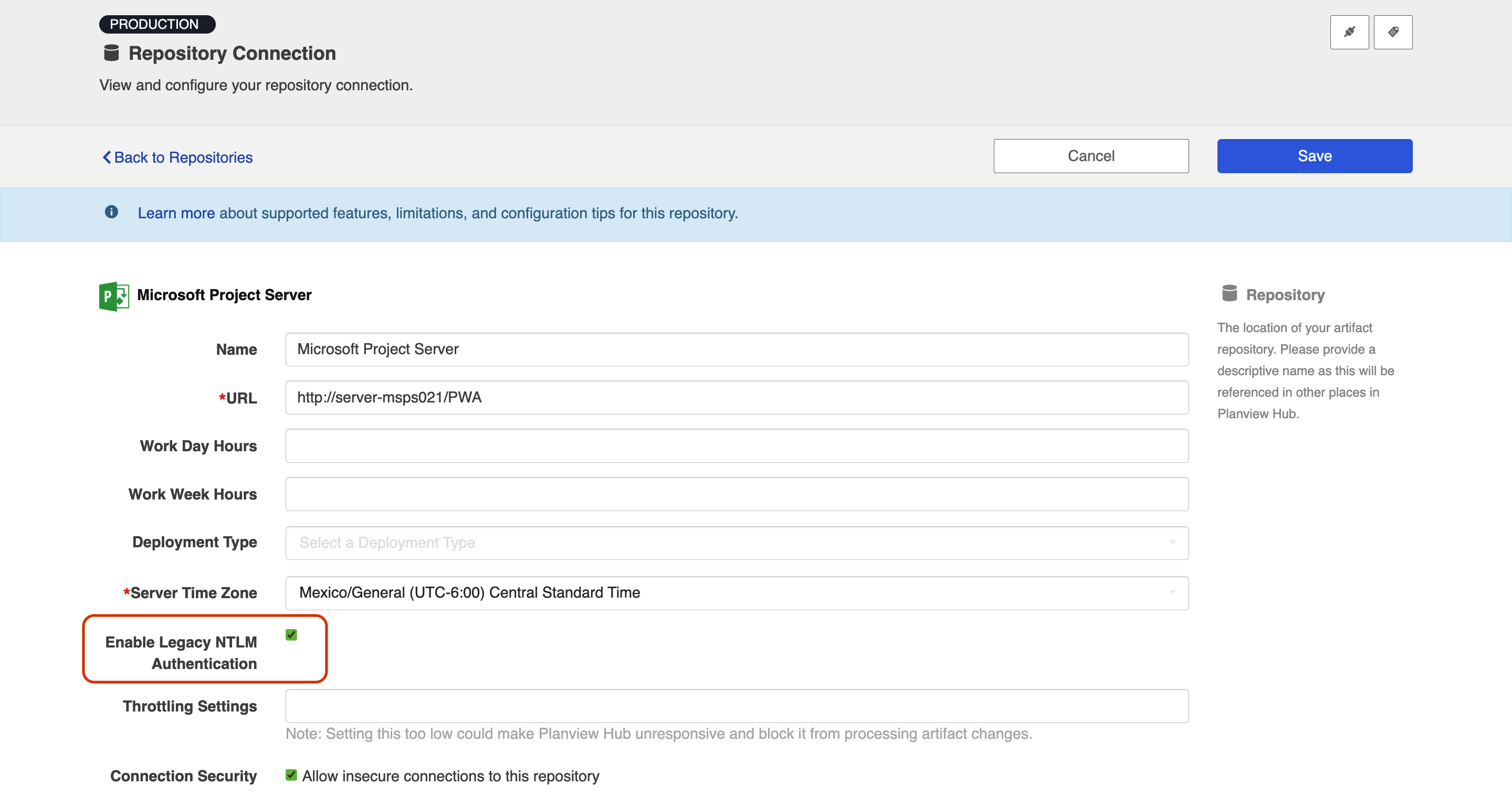
- For existing connections, the new “Enable Legacy NTLM Authentication" checkbox is checked:
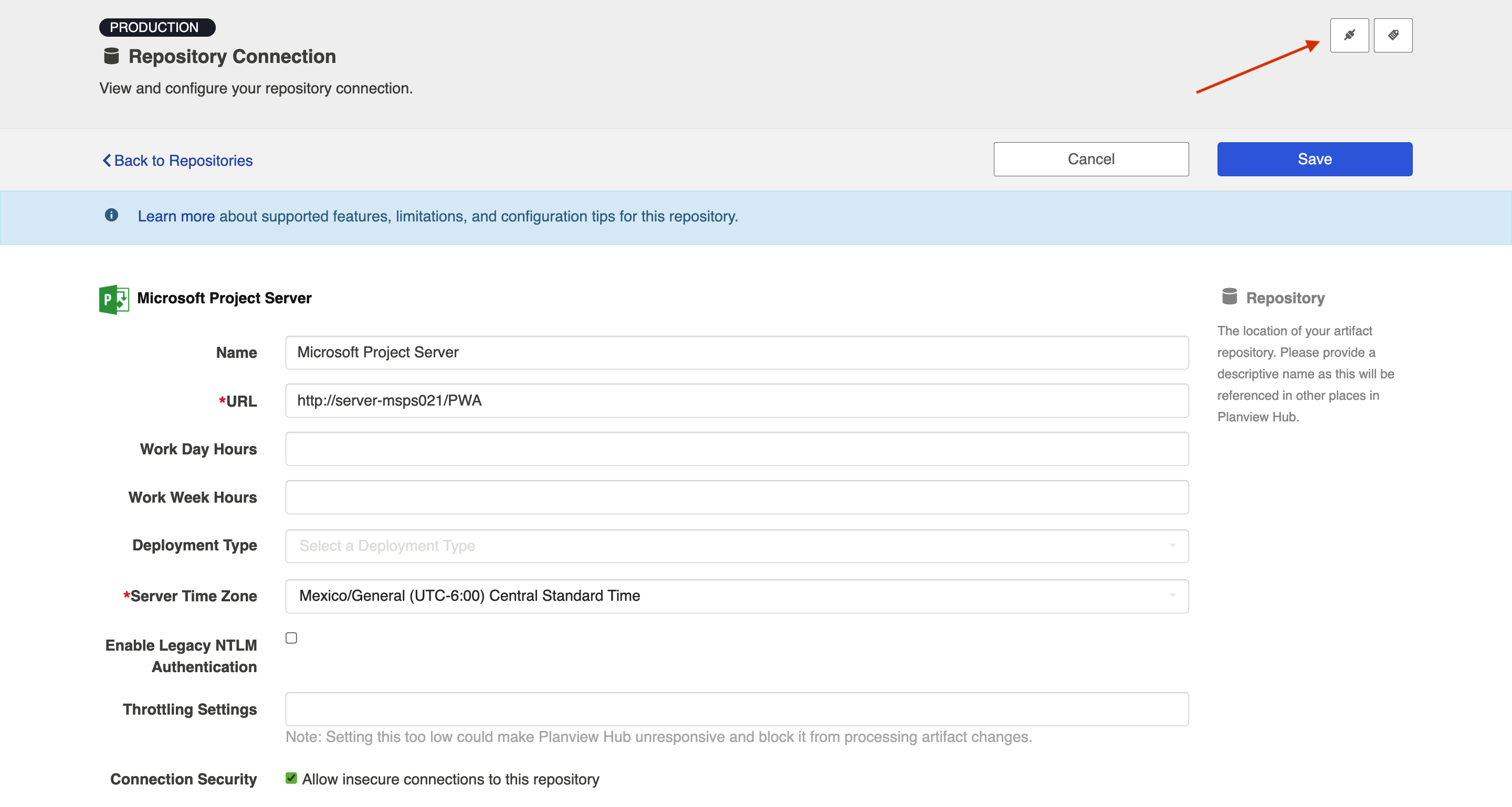
- Uncheck the checkbox and click the Test Connection button:
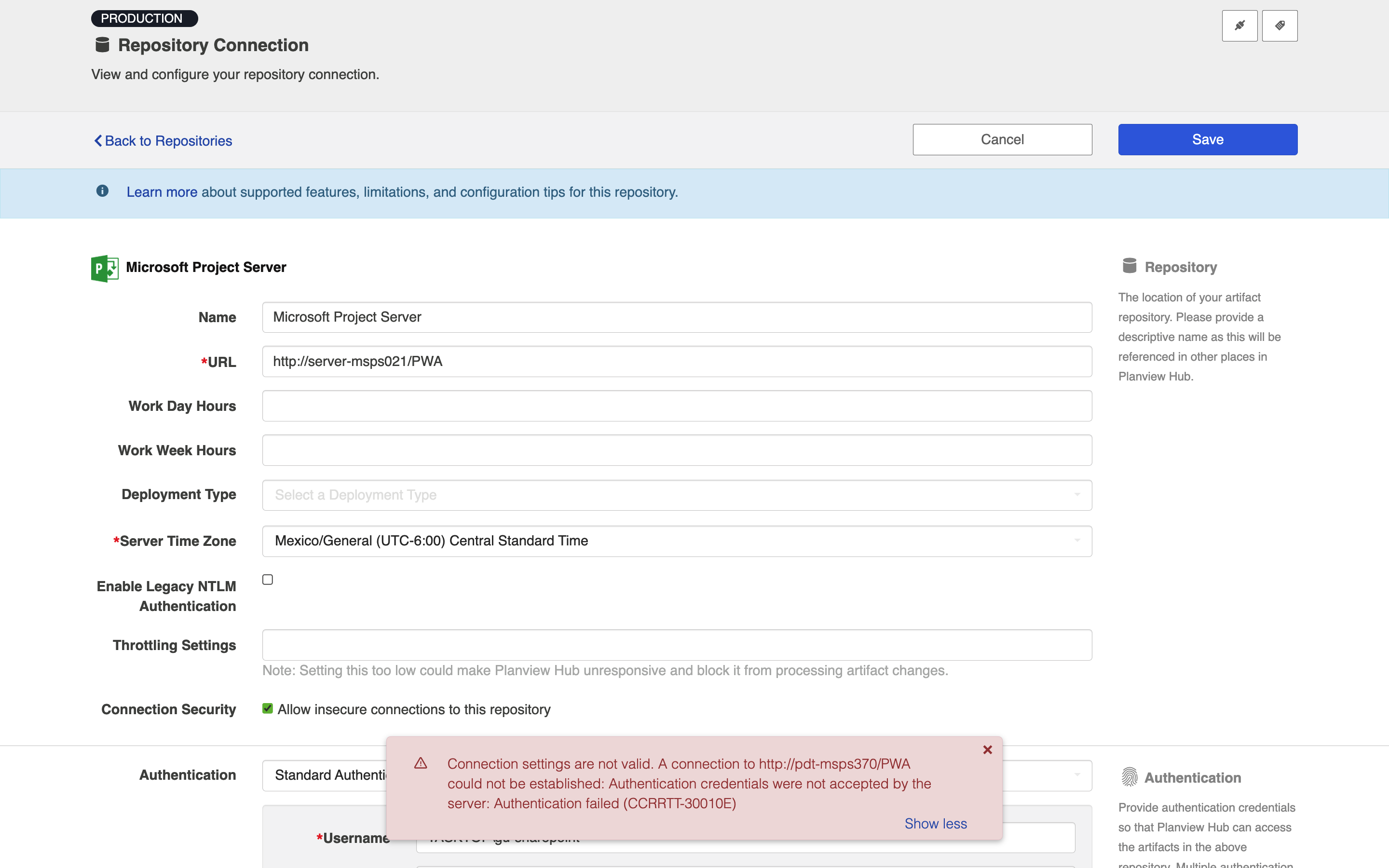
- If your repository requires the use of NTLM, an error message similar to the one in the screenshot below will appear. In this case, your administrator is required to enable a non-NTLM-based authentication before the deprecation date (see below)
- For SharePoint and ProjectServer, your administrator must reconfigure the web server (IIS) to support Basic authentication.
- For ADO, Microsoft encourages Personal Access Token (PAT) authentication instead of reconfiguring IIS for Basic Authentication.
- Unlike the Microsoft connectors, authentication scheme support depends on how Digital.ai Agility was installed. Supporting more secure authentication methods requires running the application installer. Similar to Microsoft, Digital.ai recommends using access token authentication instead of Basic Auth because support for the latter may be removed in a future release.
- If you are not using NTLM (i.e., the checkbox is not enabled for your normal operation), or the error does not appear when validating the connection (with the checkbox enabled), no further action is required.
What if I need more time?
Our support team will be able to extend the usage of NTLM on a case by case basis for a short period of time in the rare case that repositories only support NTLM based authentication, and more time is needed to add support for more secure authentication methods. Please contact our support team if necessary.
Appendix
What is NTLM?
NTLM is an authentication protocol — a defined method for helping determine whether a user who’s trying to access an IT system really is actually who they claim to be.
How NTLM authentication works
NTLM doesn’t send passwords directly over the network - instead it sends a password hash. A password hash is created by a hashing algorithm - a function that transforms a password into a different string of characters. The function is repeatable: the same password will always generate the same hash. It’s also one-way: it’s easy to transform a password into a hash, but there’s no way to transform the hash back into the password.
What’s the problem with NTLM authentication?
NTLMv1 is a very weak authentication protocol by today’s standards. And while v2 is much more secure than v1, it’s still not nearly as secure as more modern protocols.
Because of the weak encryption standards used in both NTLMv1 and NTLMv2, it is possible for a malicious actor to use brute force methods to determine the password from the hash. As a result, even in a fully patched system, NTLMv1 and NTLMv2 authentication are vulnerable to various malicious attacks, including SMB replay, man-in-the-middle attacks, and brute force attacks.
Additional Resources
- Microsoft advises using Kerberos (primary authentication method since Windows 2000) instead of NTLM.
- Microsoft documentation describing vulnerabilities with NTLM.
- NTLM authentication: What it is and why you should avoid using it
- NTLM Explained: Definition, Protocols & More | CrowdStrike